Embark on a journey into the fascinating realm of elements, the fundamental building blocks of our universe. Select all the statements that correctly describe elements, as we delve into their unique properties, reactivity, and significance in shaping our world.
From the smallest subatomic particles to the largest celestial bodies, elements play a crucial role in the tapestry of existence. Understanding their characteristics and behavior is essential for unraveling the mysteries of chemistry, physics, and the natural world around us.
Definition of Elements
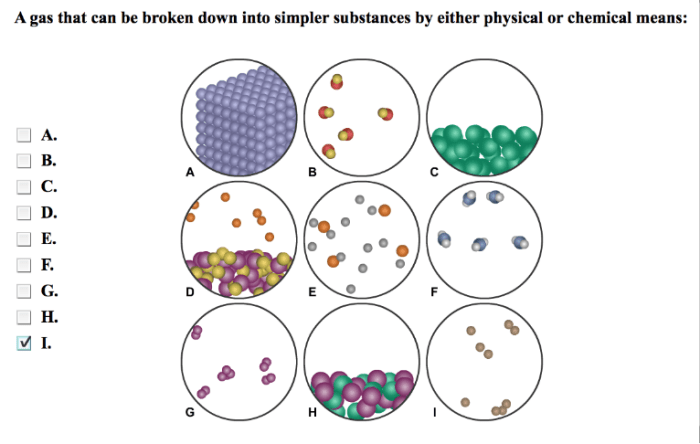
Elements are the fundamental building blocks of matter and the basic units of the periodic table. They are pure substances that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means.
Each element is characterized by its atomic number, which represents the number of protons in its nucleus. The atomic number determines the element’s identity and its position on the periodic table.
Examples of elements include hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), sodium (Na), and gold (Au).
Characteristics of Elements
Physical Characteristics
The physical characteristics of elements include their appearance, density, melting point, boiling point, and electrical conductivity.
- Metals are typically shiny, malleable, and ductile.
- Non-metals are typically dull, brittle, and poor conductors of electricity.
Chemical Characteristics
The chemical characteristics of elements determine their reactivity and the types of compounds they form.
- Metals tend to lose electrons easily, making them good reducing agents.
- Non-metals tend to gain electrons easily, making them good oxidizing agents.
Reactivity of Elements

The reactivity of elements refers to their tendency to undergo chemical reactions. Highly reactive elements are more likely to form compounds with other elements, while non-reactive elements are less likely to react.
Highly Reactive Elements, Select all the statements that correctly describe elements
Examples of highly reactive elements include sodium (Na), potassium (K), and fluorine (F).
Non-Reactive Elements
Examples of non-reactive elements include gold (Au), platinum (Pt), and helium (He).
Importance of Elements: Select All The Statements That Correctly Describe Elements
Elements are essential for life and play a crucial role in various industries.
- Oxygen (O) is essential for respiration and is found in the air we breathe.
- Carbon (C) is the basis of all organic compounds and is found in all living organisms.
- Silicon (Si) is used in the production of computer chips and solar panels.
Organization of Elements
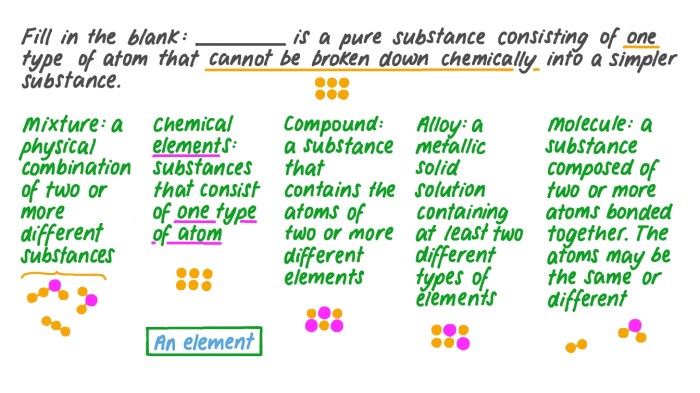
The elements are organized in the periodic table according to their atomic number and chemical properties.
The periodic table is divided into groups (vertical columns) and periods (horizontal rows).
Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties, while elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells.
Compounds and Elements
Elements are pure substances, while compounds are substances composed of two or more elements chemically combined.
Compounds have different properties from the elements they are composed of.
For example, water (H 2O) is a compound composed of hydrogen and oxygen. Water has different properties than hydrogen or oxygen alone.
History of Element Discovery
The history of element discovery dates back to ancient times, with the discovery of gold, silver, and copper.
In the 18th century, scientists began to use chemical methods to identify and isolate new elements.
In the 19th and 20th centuries, the periodic table was developed, which helped to organize and predict the properties of elements.
Today, new elements are still being discovered, often through the use of particle accelerators.
User Queries
What is the definition of an element?
An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means.
How are elements organized in the periodic table?
Elements are organized in the periodic table based on their atomic number, which is the number of protons in their nucleus.
What is the most reactive element?
Fluorine is the most reactive element.
What is the least reactive element?
Helium is the least reactive element.
What are some examples of elements?
Hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and iron are some examples of elements.